How to load StrainSEEK® Variant Call Format (VCF) files into the Comparative Genomics (CoGe) Platform
VCF files from Medicinal Genomics are generated by mapping sequencing reads (FASTQ files) to the Jamaican Lion reference (FASTA file) that Medicinal Genomics released publicly. The Jamaican Lion reference can be accessed using the CoGe platform.
Step 1 - Create a CoGe Account
CoGe provides step by step instructions for how to do this. These instructions can be accessed here:
https://genomevolution.org/wiki/index.php/How_to_get_a_CoGe_account
There are also several tutorials available to help you learn all about CoGe https://genomevolution.org/wiki/index.php/Tutorials
Step 2 - Download your raw data from Kannapedia®
Here is a publicly accessible Kannapedia entry we can use as an example:
http://www.kannapedia.net/strains/rsp11367/
Copy the URL for the Download VCF file link which for this example is here:
http://mgcdata.s3.amazonaws.com/SS2/vcf_JL/RSP11367_blockchain.vcf.gz
Step 3 - Create a New Experiment
From the main CoGe page (https://genomevolution.org/coge/)
Click the Load Experiment (LoadExp+) link
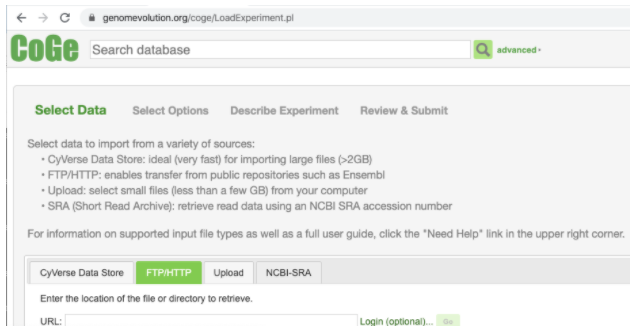
For URL enter the URL obtained from Kannapedia (Note that it is also possible to use the Upload tab if your VCF file is not publicly hosted).
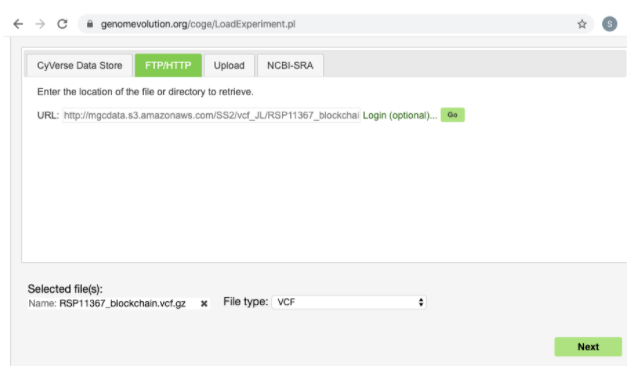
Click the Go button then scroll down and click Next
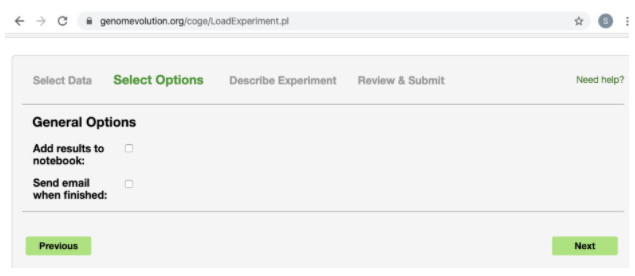
For the Options, click Next again
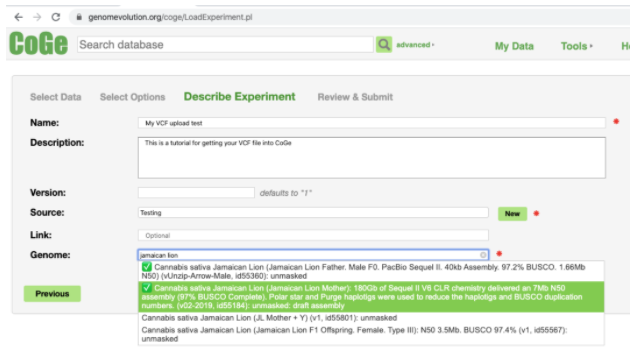
The reference currently being used to map data and call variants is:
Cannabis sativa Jamaican Lion (Jamaican Lion Mother): 180Gb of Sequel II V6 CLR chemistry delivered an 7Mb N50 assembly (97% BUSCO Complete). Polar star and Purge haplotigs were used to reduce the haplotigs and BUSCO duplication numbers. (v02-2019, id55184): unmasked: draft assembly
https://genomevolution.org/coge/GenomeInfo.pl?gid=55184
For Source click the New button and give it a name of your choosing.
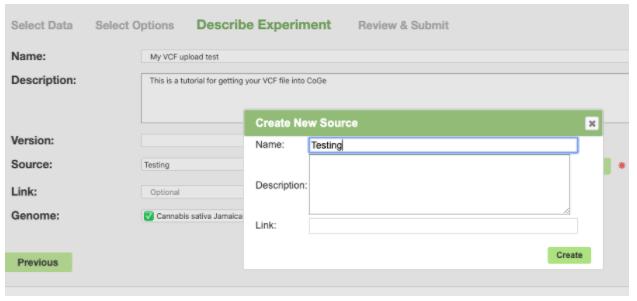
Then click Create. And finally Next.

On the Review & Submit page review the details of your experiment then click Start.
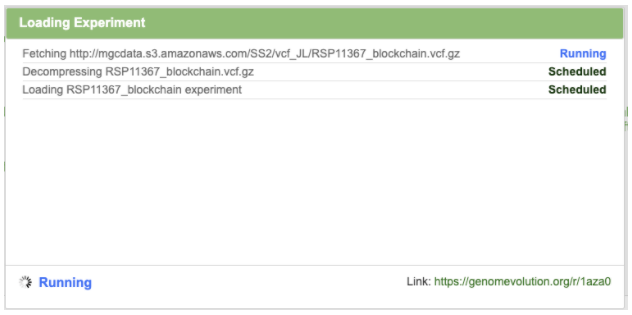
You will be directed to a page that shows details of the experiment loading. This may take several minutes to complete.
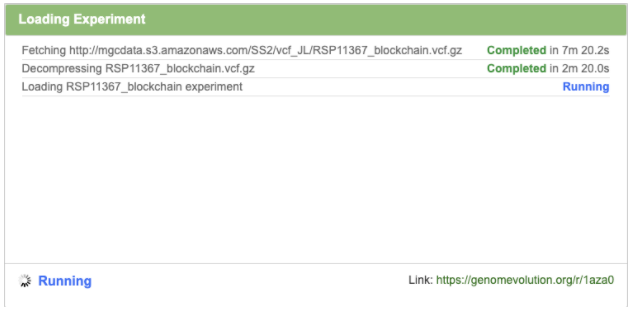
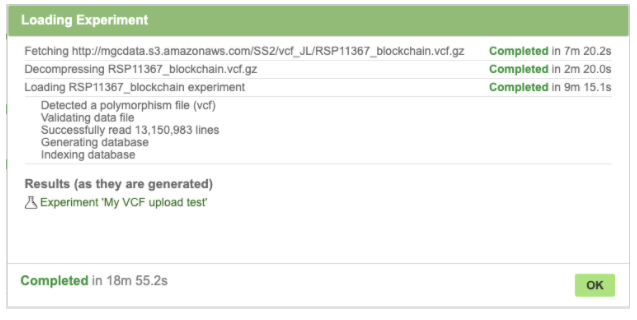
Click OK
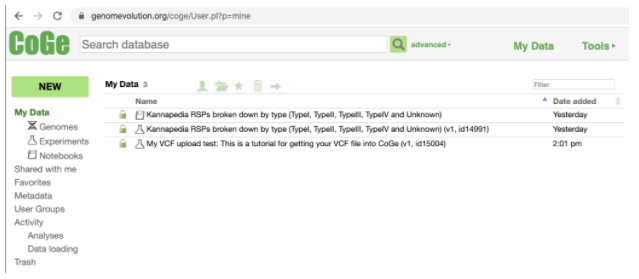
Now if you click My Data you will see your experiment has been successfully created. Your VCF has now been uploaded into CoGe and you will be able to see it visually represented in the genome browser.
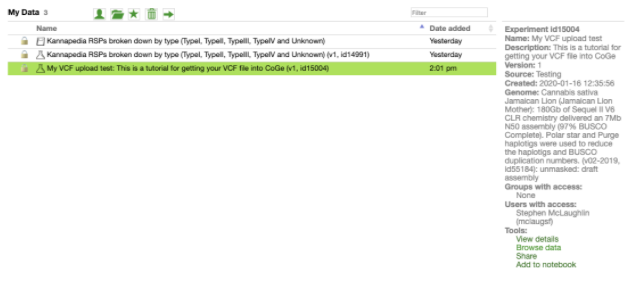
Step 4 - View your variants in the Genome Browser
Select the experiment and details will appear in the box to the right of the selection. At the bottom of these details there is a Tools section. To view your VCF file in the browser, click on Browse data.
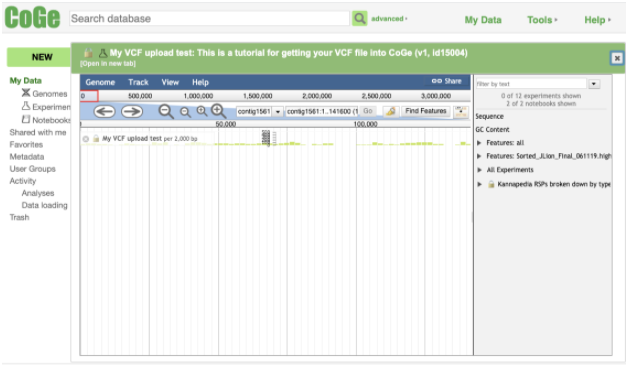
A pop up will open; this is the genome browser.
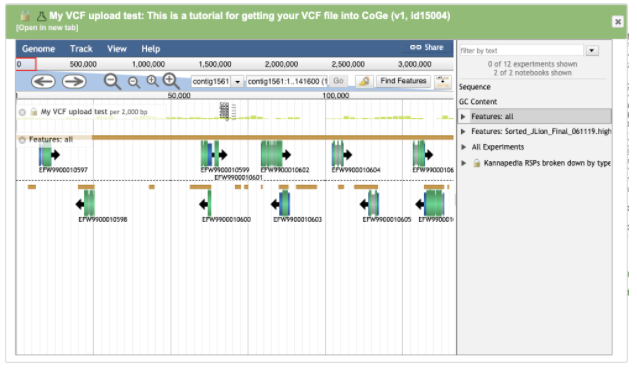
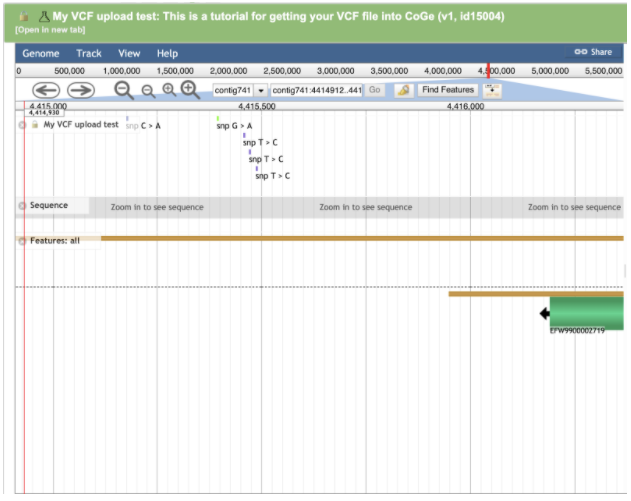
Click Features: all to turn on the genome annotation track.
Mouse over a region of interest to zoom in:
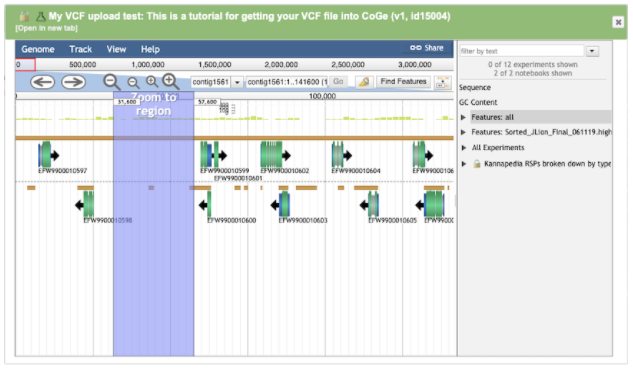
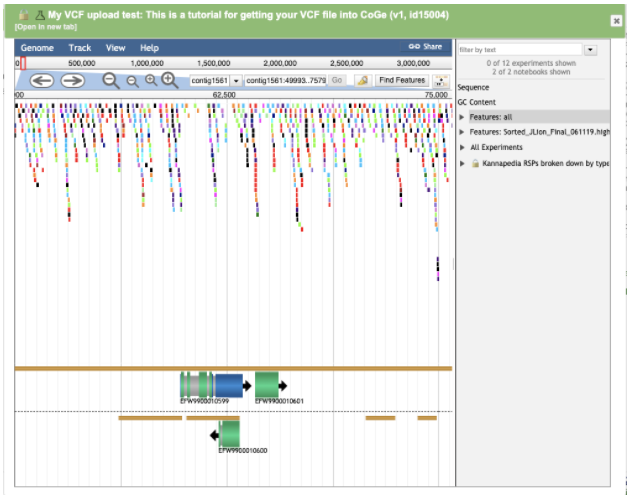
Zooming into the variants shows each variant represented as an individual colored dot overlayed with the Jamaican Lion annotation track.
Click on an individual variant to expose additional variant-level detail:
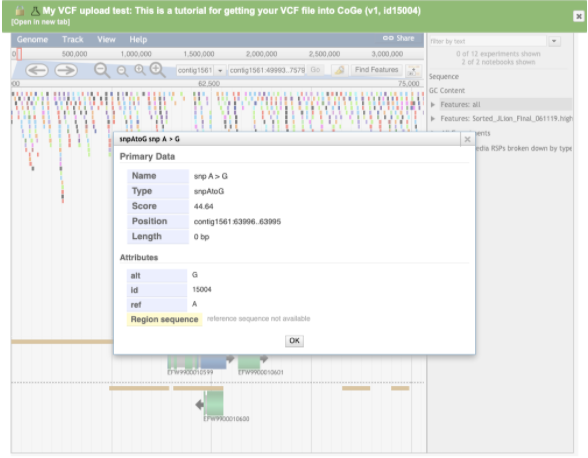
Step 5 - Navigate to a region of interest
The Cannabis genomes Medicinal Genomics published in CoGe have annotations available that came out of the program Maker. Maker assigned accessions to annotated regions starting with the prefix EFW*. EFW IDs can be seen in the genome browser screenshots above aligning with variants in the VCF file. If you know the accession you’re interested in, you can browse right to it.
We are working on making the annotation more easily searchable in CoGe. For the time being, it is recommended to consult the annotation in this spreadheet:
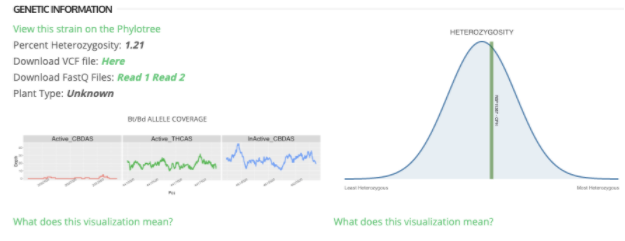
Here are the accessions for CBDAS and THCAS used in the Bt/Bd ALLELE COVERAGE coverage plots in the StrainSEEK® report:
active CBDAS: ID=EFW9900013020
active THCAS: ID=EFW9900002719
inactive CBDAS: ID=EFW9900002721
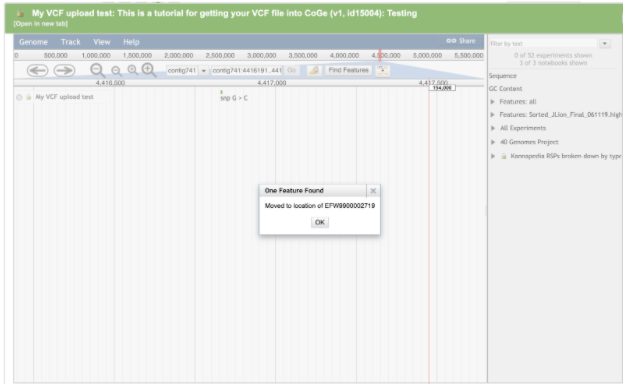
For example, to navigate to THCAS (EFW9900002719) click the Find Features button
Enter the accession EFW9900002719 for THCAS in the search box
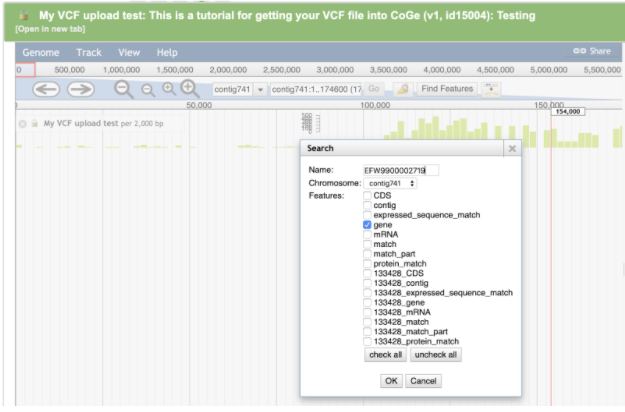
Click the OK button
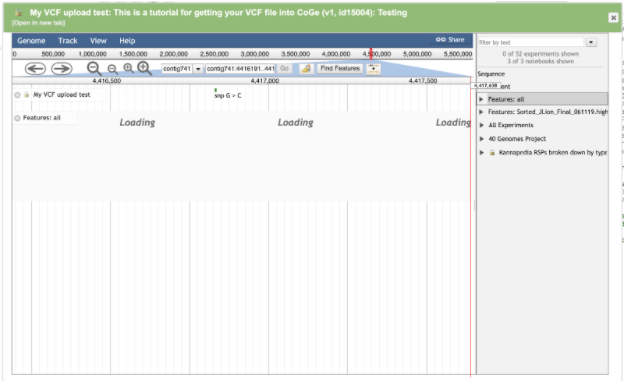
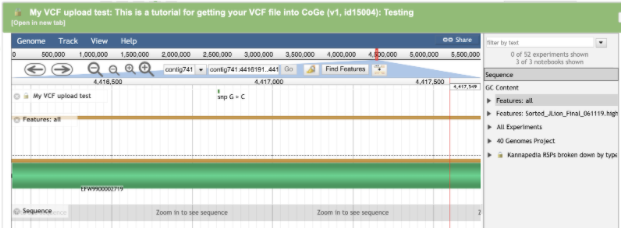
Make sure to click on the Features: all link on the right hand side. This will turn on the annotation track of the browser so that overlaps between the variants and THCAS can be observed. You may also want to click on the Sequence track at the same time
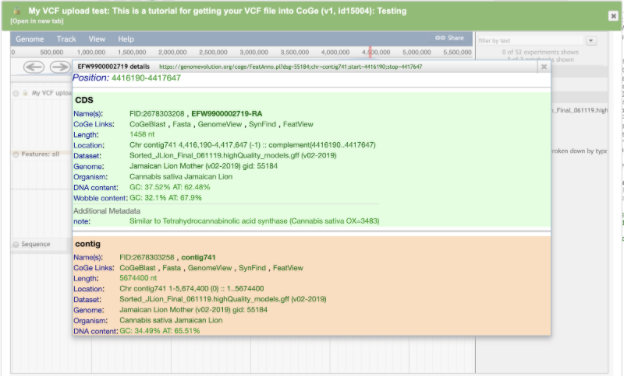
Clicking on the green-colored EFW9900002719 block will show annotation details for this gene
Here are some SNPs upstream of THCAS